The Link Between Bad Teeth and Heart Disease Will Shock You!
Your oral health and heart health are more connected than you’d think. When you have gum disease, harmful bacteria can enter your bloodstream through infected gums and attach to fatty plaques in your arteries. This dangerous process restricts blood flow and increases your risk of heart attack and stroke. Studies show people with periodontal disease are 2-3 times more likely to experience cardiovascular problems. Understanding this vital connection could save your life.
Understanding the Mouth-Heart Connection
While many people view oral health and heart health as separate concerns, research shows they’re closely linked through inflammation and bacteria. When you don’t maintain good oral hygiene, harmful bacteria in your mouth can enter your bloodstream through infected or bleeding gums.
These bacteria can trigger inflammation throughout your body, including your heart vessels. Your mouth serves as a gateway to your cardiovascular system, and the bacteria from periodontal disease can attach to fatty plaques in your arteries.
This buildup can restrict blood flow and increase your risk of heart attack and stroke. Additionally, the chronic inflammation from gum disease can weaken your blood vessels and create ideal conditions for blood clots to form.
That’s why maintaining healthy teeth and gums is crucial for your heart health.
How Oral Bacteria Travels to Your Heart
When bacteria from infected gums enter your bloodstream, they can hitch a ride through your circulatory system straight to your heart. This happens every time you chew, brush, or floss, as these actions create tiny tears in your gum tissue.
If you have gum disease, the harmful bacteria can slip through these openings and travel throughout your body.
Once in your bloodstream, oral bacteria can attach to fatty plaques in your arteries, causing inflammation and narrowing of these vital pathways. They may also directly infect your heart valves, leading to a dangerous condition called endocarditis.
You’ll face an increased risk of blood clots, which could trigger a heart attack or stroke. That’s why maintaining good oral hygiene isn’t just about preventing cavities – it’s protecting your heart.
Warning Signs Your Teeth Are Affecting Your Heart
Could your teeth be sending distress signals about your heart health? Pay attention to these warning signs that suggest oral bacteria might be affecting your cardiovascular system.
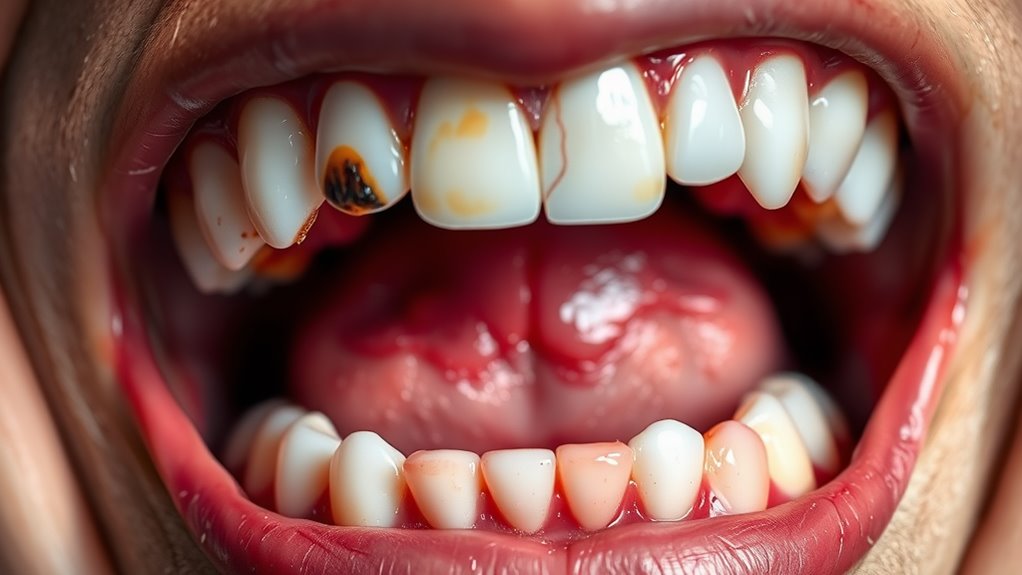
If you notice bleeding gums, swollen gums, or persistent bad breath, you’re experiencing common indicators of periodontal disease. These symptoms often signal that bacteria are actively damaging your oral tissues and potentially entering your bloodstream.
You’ll also want to watch for loose teeth, receding gums, or teeth that appear longer than usual.
Other red flags include jaw pain combined with chest discomfort, which might indicate inflammation affecting both areas. If you have a family history of heart disease and notice these dental issues, don’t wait to seek help.
Your dentist and doctor should work together to assess your risk factors.
Research and Scientific Evidence
Scientific studies over the past two decades have revealed a strong connection between oral bacteria and heart disease. Research shows that the same bacteria found in infected gums can travel through your bloodstream and attach to your heart’s blood vessels, leading to inflammation and potential blockages.
A landmark study in the Journal of the American Heart Association found that people with periodontal disease were 2-3 times more likely to experience a heart attack or stroke.
Other studies have linked specific oral bacteria, particularly P. gingivalis, directly to arterial plaque formation. Your oral health significantly impacts your cardiovascular system, as researchers at Harvard Medical School discovered that treating gum disease can lower systemic inflammation markers associated with heart disease.
Prevention Methods and Daily Oral Care
To prevent the devastating link between poor oral health and heart disease, you’ll need to maintain a consistent dental care routine.
Brush your teeth twice daily using fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled brush. Don’t forget to floss at least once daily to remove bacteria-laden plaque between teeth.
Replace your toothbrush every three months and schedule regular dental cleanings twice a year. Cut back on sugary foods and drinks that feed harmful bacteria, and quit smoking to reduce your risk of gum disease.
If you notice bleeding gums, sensitivity, or persistent bad breath, see your dentist immediately. These symptoms could indicate periodontal disease, which may increase your risk of heart problems.
Consider using an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria levels in your mouth.
Treatment Options and Medical Interventions
When dental problems advance to the point of affecting heart health, medical interventions often require a two-pronged approach.
You’ll need to address both your oral health and cardiovascular concerns simultaneously through coordinated care between your dentist and cardiologist.
Your treatment plan may include:
- Deep cleaning procedures to remove bacteria and plaque
- Antibiotic therapy to fight active infections
- Surgical interventions for severe periodontal disease
- Blood pressure and cholesterol management
- Heart monitoring and preventive medications
If you’ve developed heart complications, you’ll require regular checkups with both specialists.
They’ll work together to monitor inflammation levels, adjust medications, and prevent further deterioration of your oral and cardiac health.
Remember that successful treatment depends on your commitment to following their prescribed care plan.